

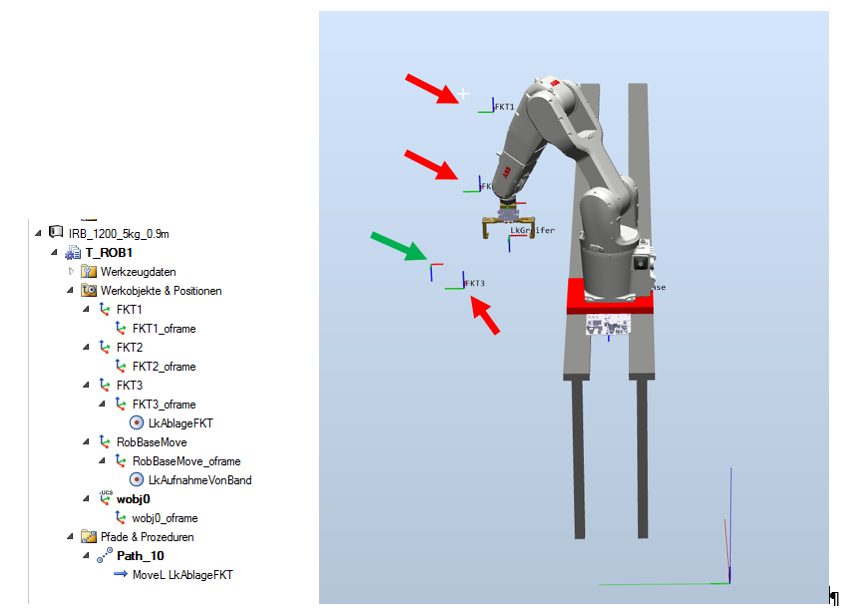
- ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS SOFTWARE
- ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS OFFLINE
- ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS FREE
Once you have used leads I and aVF to plot a graph, you need to do the following Lead I and lead aVF look at the heart in a way that gives us a horizontal and vertical axis, respectively, that we can create a 2-D graph from. I’m going to take you through the slow way, fast way and really fast way! Calculating Axis – The Slow Way

There are a few way to calculate the cardiac axis when looking at a 12 lead ECG.
Causes can include right ventricular hypertrophy, right bundle branch block, left posterior fascicular block, anterolateral myocardial infarction, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, ventricular tachycardia and/or dextrocardia.Right axis deviation = QRS axis between +90 to +180 degrees.Causes can include left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle branch block, left anterior fascicular block, inferior myocardial infarction, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, ventricular tachycardia and/or ventricular paced rhythm.Left axis deviation = QRS axis between -30 to -90 degrees.A cardiac axis deviation is not normal and usually prompts the clinician analysing the ECG to have a closer look. If something within the heart causes the electrical conduction to deviate from its normal path, we refer to this as a cardiac axis deviation. Therefore, we say that the normal electrical conduction flow within the ventricles (normal cardiac QRS axis) is anywhere between -30 degrees to +90 degrees. Think of the image below as if we have superimposed a graph over the top of the heart, thereby allowing us to see a 2-D representation of where the majority of electrical flow is heading as it depolarises the ventricles. If we think about the flow of electrical conduction through the heart, the majority of electrical conduction will head towards the left ventricle as there is more muscle to depolarise. This is where the cardiac axis +/- deviation comes into play.
ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS SOFTWARE
The software will automatically create sufficient number of targets in a path to make sure the path precisely matches the machining requirement.If our electrical conduction pathway stays constant and our lead viewpoint changes (comparing one lead to another lead), each lead will reflect the electrical flow in relation to itself thereby showing different waveforms. If our viewpoint stays constant (same lead) and the electrical conduction within the heart changes its pathway, the lead waveform will change to reflect this. As the targets and paths are automatically generated either from CAD surfaces or CAM code, a consistent and accurate result can be achieved independent of user skills. The different path strategies increase the tool life time by machining with a tool area instead of a single point and cover also different tool contact point for different processes. The integrated postprocessor generates accurate robot paths from the CAM software and utilizes the strength of being closely integrated into the robot controller.Įxtended tool life time and improved path accuracy.

ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS FREE
It can also be used with other CAD/CAM-based applications.It provides several strategies to easily generate machining paths and curves on free surfaces to run the machining program, satisfying different path generation requirements. The Machining PowerPac is the ideal tool for programming of applications such as machining, deburring, grinding, polishing and deflashing. With its new programming methods, ABB is setting the standard for robot programming worldwide.
ROBOTSTUDIO DEFINE EXTERNAL AXIS OFFLINE
RobotStudio is the leading product for offline programming on the market. Increased engineering efficiency within machining applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
